
When cooking different dishes, it is important to set your oven at the correct temperature. That way you can ensure your food is cooked correctly, creating delicious meals for you and your family. Several temperature systems are used around the world, as well as depending on the type of oven you have, the choice of temperature will vary.
Celsius degree (symbol: °C) is the unit of temperature on the Celsius scale, based on 0° for the freezing point of water and 100° for the boiling point of water. The Ceslius scale is used in the countries where the metric system of units has been adopted.
The following formula can be used to convert a temperature on the Fahrenheit (°F) scale to the Celsius (°C) value: =(°C * 9) / 5 + 32.
For example: 180 °C = (180 * 9) / 5 + 32
= 1620 / 5 + 32
= 324 + 32
= 356 °F
Fahrenheit degree (symbol: °F) is the unit of temperature on the Fahrenheit scale, based on 32 °F for the freezing point of water and 212 °F for the boiling point of water. The Fahrenheit temperature scale is used in the United States, its territories and associated states, as well as the (British) Cayman Islands and Liberia for everyday applications.
The following formula can be used to convert a temperature on the Celsius scale to the Fahrenheit value: =(°F – 32)*( 5 / 9)
For example: 400 °F = (400 – 32) * (5 / 9)
= 368 * 0.56
= 204 °C
The gas mark is a temperature scale used on gas ovens and cookers in the United Kingdom, Ireland and some Commonwealth of Nations countries.
Gas mark 1 is 275 degrees Fahrenheit (135 degrees Celsius). Oven temperatures increase by 25 °F (13.9 °C) each time the gas mark increases by 1.
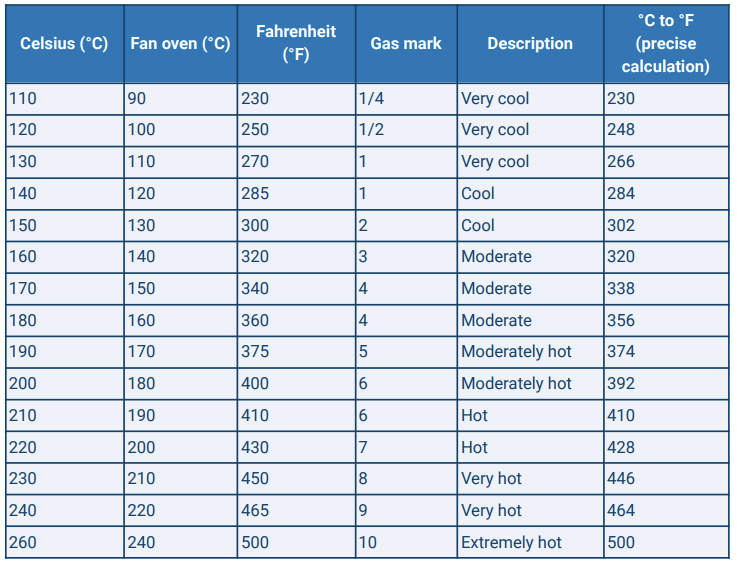
Here is a chart to help you easily convert between Celsius, Fahrenheit and Gas Mark for the most common temperatures used in the kitchen.
How do I know what oven I have – conventional or fan oven?
A conventional oven has two heating elements for heating air inside the oven, usually located on the bottom and on top inside the oven. The heat from these elements warms the air inside the oven. The bottom heating element is the main source of heat and is ideal for roasting large cuts of meat. The upper heating element delivers top-down heat and works best for broiling and browning dishes. The middle rack may be considered the “default” position.
Conventional ovens do not have a fan to circulate the air in the oven, therefore placement of the dishes in the oven is important and they might need to be rotated to achieve the best results.
Fan-assisted ovens or fan ovens have a heat element and a fan at the back of the oven’s compartment. The fan circulates the hot air throughout the oven. This helps the dishes in the oven to cook more evenly and at lower temperatures. For fan ovens the fan runs constantly while you are cooking. For fan-assisted ovens you can choose to cook with the fan or without.
Fan oven cooking temperatures are typically around 20°C less than for conventional ovens because the fan circulates the hot air inside the oven and into the food, ensuring a more even temperature.
